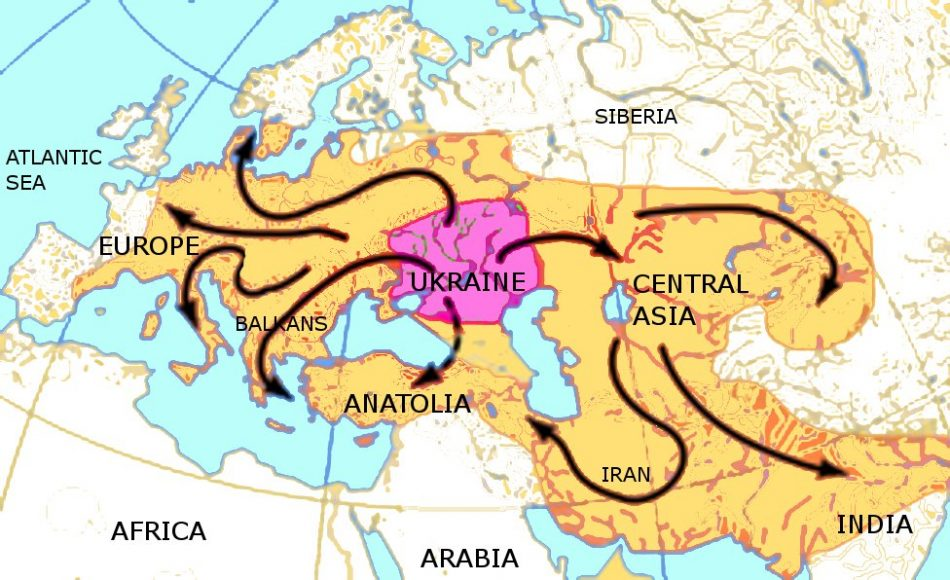
The origins of Indo-European languages are a fascinating subject of study, revealing the roots of over 400 languages spoken by nearly 40% of the global population today. Recent landmark studies have identified the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in present-day Russia approximately 6,500 years ago, as the likely originators of these ancient tongues. These individuals, associated with the renowned Yamnaya culture, played a pivotal role in the linguistic evolution that has shaped multiple languages across Europe and Asia. Ancient DNA studies have provided compelling evidence that this population not only spoke proto-Indo-European but also intermingled with various other cultures in the region, further influencing the development of languages. As we delve into this intricate narrative, we uncover the profound impact of these early communities on modern linguistic landscapes.
Exploring the foundation of the Indo-European language family unveils a complex tapestry of linguistic history, originating from a group of ancient individuals whose migrations and interactions sparked widespread communication across vast territories. This ancestry is traced back to groups inhabiting regions like the lower Volga, known for their distinctive cultural practices, including those of the Yamnaya society. The study of these ancient lineages, reinforced by advancements in genetic research, reveals a rich framework of migration and exchange that contributed to the early formation of European and Asian languages. By examining this intricate web of interactions and influences, we can better understand how the proto-Indo-European language evolved and gave rise to the diverse tongues we recognize today.
The Genetic Legacy of Caucasus Lower Volga People
The Caucasus Lower Volga people played a pivotal role in shaping the demographic and linguistic landscape of Europe and Asia. Recent studies, bolstered by advanced ancient DNA analyses, reveal that these populations, residing around 6,500 years ago in present-day Russia, were a melting pot of diverse genetic lineages. These early inhabitants are considered the precursors to the Yamnaya culture, known for their significant contributions to the spread of proto-Indo-European languages. By identifying genetic connections among various ancient populations, researchers provide compelling evidence of the intricate web of migrations and cultural exchanges that characterized early human history.
Moreover, these findings challenge traditional narratives and offer a fresh perspective on how languages evolved. The research indicates that the Caucasus Lower Volga people not only influenced the linguistic heritage of Indo-European speakers but also interacted with neighboring cultures, thus enriching their own genetic makeup. This dynamic interplay of peoples and languages is crucial in understanding the origins of more than 400 modern tongues that trace their ancestry back to these early groups, highlighting the profound impact of genetic studies in reconstructing our past.
Insights from Ancient DNA Studies
Ancient DNA studies have revolutionized our comprehension of linguistic evolution, particularly concerning the origins of the Indo-European languages. By analyzing DNA samples excavated from archaeological sites in Eastern Europe, researchers have discerned significant links between various ancient populations, including the prominent Yamnaya culture. This genetic evidence supports the long-held steppe hypothesis, which postulates that early Indo-European speakers migrated from the Eurasian steppes, initiating waves of cultural and linguistic diffusion across Europe and into parts of Asia.
The knowledge gained from ancient DNA research has unveiled a complex tapestry of historical migration patterns, revealing how interconnected human populations were during prehistoric times. For instance, through the study of the Yamnaya group, scientists have traced the spread of agricultural practices, technologies, and languages, demonstrating how these aspects of culture were not static but rather fluid and adaptable. As a result, our understanding of how Indo-European languages disseminated and evolved can now be viewed through a wider lens, taking into account the genetic influences that shaped them.
The Role of the Yamnaya Culture in Linguistic Spread
The Yamnaya culture has long been regarded as a cornerstone in the narrative of Indo-European language evolution. Originating from the steppe regions of Eastern Europe, the Yamnaya people are credited with pioneering advancements that allowed for the dissemination of their language across vast distances. As adept pastoralists and innovators of horse-drawn transportation, they facilitated trade and interaction with neighboring civilizations, thereby enhancing the spread of their proto-Indo-European tongue and its derivatives.
As the Yamnaya expanded their territory, they encountered diverse groups and cultures, leading to significant genetic and linguistic exchanges. Their nomadic lifestyle allowed them to traverse great distances, reaching as far as Ireland and Central Asia. Through intermarriage and cultural assimilation with local populations, the Yamnaya further propagated their language and customs, leaving a legacy that continues to influence several languages in Europe and beyond. Understanding the Yamnaya’s role in this historical context provides a clearer picture of how languages and cultures evolve over time.
Cultural Traditions and Burial Practices of Indo-European Speakers
The continuity of cultural practices, particularly burial traditions, sheds light on the shared identity among the Indo-European speakers. The Yamnaya culture, for instance, is known for its distinctive burial mounds, or kurgans, which were utilized for the interment of their deceased. This ritual not only reflects the Yamnaya’s cultural values but also serves as a critical archaeological marker that helps researchers trace the movement and influence of these populations throughout history.
Kurgans became significant sites for later cultures, indicating the persistence of these burial practices as they were adopted by or influenced subsequent groups. The emphasis on such elaborate burial techniques speaks to a belief system surrounding death and the afterlife. As a result, studying these traditions not only enriches our understanding of the Yamnaya culture itself but also informs us about the broader Indo-European heritage that has persisted over millennia.
How Linguistic Evolution Reflects Population Dynamics
The evolution of languages often parallels shifts in population dynamics, reflecting how groups of people interacted, merged, or diverged over time. In the case of the Indo-European family, researchers have identified patterns that correlate with historical migrations, conflicts, and trade. Each wave of migration brought new influences into the existing linguistic landscape, showcasing how languages are living entities that adapt and transform in response to external factors.
For example, the Yamnaya expansion across Europe and into South Asia illustrates how linguistic evolution is not merely a result of geographical separation but is also driven by social interactions. As peoples came into contact, their languages amalgamated, borrowed, and restructured. Thus, understanding these dynamics is essential to grasp the complexities of linguistic origins, enabling linguists and geneticists alike to reconstruct the narratives of human history.
The Impact of the Russia-Ukraine War on Research Collaboration
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict presents unique challenges for researchers collaborating on studies related to ancient DNA and linguistic evolution. With tensions impacting academic relationships, collaborative efforts have become fragmented, affecting the sharing of crucial data necessary for advancing research. For instance, the division of findings regarding the Indo-European language origins has highlighted the difficulty of cross-border scholarly work in the current political climate.
Despite these challenges, researchers are determined to continue their investigations, albeit with the complexities of navigating geopolitical landscapes. The commitment to uncovering the roots of the Indo-European languages persists, as it represents not only an academic pursuit but also an endeavor to bridge historical divides. This commitment underscores the importance of science as a unifier in promoting understanding amidst conflict.
Tracing the Genetic Footprint of Indo-European Languages
A significant aspect of the latest research into Indo-European languages is tracing the genetic footprints left by ancient populations. By examining the DNA of individuals from different archaeological sites, scientists can chart the movements and interactions of peoples who spoke these languages. This aspect is particularly vital in providing evidence for the connections hypothesized in linguistic studies, enriching our understanding of how languages spread and evolved over time.
The methodology employed by researchers in these studies involves rigorous genetic testing and comparative analysis of ancient and modern DNA. By mapping genetic similarities, they can track the ancestry of various populations, discovering links between the Caucasus Lower Volga people, Yamnaya, and modern European and Asian populations. The findings not only confirm linguistic theories but also illustrate how deeply intertwined our genetic past is with our linguistic heritage.
The Intersection of Archaeology and Linguistics in Understanding Origins
The intersection of archaeology and linguistics provides valuable insights into the origins and evolution of languages. Archaeological findings, such as artifacts and burial sites like kurgans, serve as critical data points that inform linguistic hypotheses about the populations that inhabited those regions. These cultural remnants offer evidence of social structures, practices, and technologies that existed alongside language development, creating a holistic understanding of human history.
Through careful excavation and analysis, archaeologists can uncover patterns that complement linguistic research, shedding light on how language may have functioned in sociocultural contexts. The collaboration between these disciplines enhances our overall comprehension of ancient societies, emphasizing the importance of an interdisciplinary approach in reconstructing the narratives of our ancestors.
The Future of Indo-European Languages: Genetic Studies Ahead
Looking ahead, the future of research into Indo-European languages appears promising, particularly with advancements in genomic technologies. The field is poised for significant breakthroughs that will continue to unravel the complexities of linguistic evolution and population dynamics. Ongoing studies are expected to focus on deeper genetic analyses, including examining ancient samples that could provide further insights into previously unidentified lineages and their languages.
As researchers delve deeper into the genetic histories of various groups, it is likely that new connections among languages will emerge, enhancing our understanding of their development and spread. The integration of cutting-edge technology with traditional methods will pave the way for more comprehensive studies. This evolution in research not only has implications for linguistics but also for our understanding of human history as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the origins of the Indo-European language family?
The origins of the Indo-European language family are traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga region in present-day Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. Studies have identified these early speakers as the ancestors of numerous languages spoken today, revealing links to the Yamnaya culture.
How do ancient DNA studies contribute to our understanding of Indo-European language origins?
Ancient DNA studies provide crucial evidence for pinpointing the origins of Indo-European languages. These studies have revealed genetic links between the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya culture, highlighting the complex demographic changes that occurred as these groups spread their languages across Europe and Asia.
What role did the Yamnaya culture play in the spread of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture is believed to have played a pivotal role in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages around 5,000 years ago. Their innovations in pastoralism and transportation facilitated their movement westwards, resulting in a widespread influence on the languages of Europe and beyond.
What is the significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga people in the study of Indo-European language origins?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people are significant as they are identified as the probable originators of proto-Indo-European languages. Their genetic makeup, revealed through extensive studies, indicates a foundational role in shaping the linguistic diversity that emerged later in Europe and the Indian subcontinent.
How does linguistic evolution relate to the findings about the Indo-European language family?
Linguistic evolution, as revealed through connections among languages like Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, reflects the historical migrations and interactions of people originating from the Caucasus Lower Volga region. These findings illustrate how the proto-Indo-European language diversified and evolved over thousands of years due to cultural and genetic exchanges.
What were the demographic impacts of the Yamnaya people on European populations?
The Yamnaya people caused significant demographic shifts in Europe, with evidence of a massive population replacement in various regions. Genetic studies suggest that they intermingled with local populations, leading to the widespread adoption of the Indo-European languages across diverse communities.
What are the implications of discovering the links between Yamnaya culture and Indo-Anatolian speakers?
Discovering the connections between Yamnaya culture and Indo-Anatolian speakers enhances our understanding of the geographical spread of Indo-European languages. It suggests that these groups shared cultural and linguistic traits, further supporting the theory of a broader proto-Indo-European language network.
How do researchers utilize archaeological data in conjunction with genetic findings regarding Indo-European languages?
Researchers integrate archaeological data, such as burial sites and cultural relics, with genetic findings to construct a comprehensive picture of Indo-European language origins. This multidisciplinary approach helps clarify population movements and cultural transformations that contributed to linguistic development.
What impact has the current geopolitical situation had on research into Indo-European language origins?
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has complicated collaborative research efforts, particularly concerning genetic studies of ancient populations. This situation has led to a division of findings from archaeological sites, impacting the collective understanding of the origins of Indo-European languages.
How did the Yamnaya people’s cultural practices influence their linguistic legacy?
The cultural practices of the Yamnaya people, such as their burial traditions and innovative transportation methods, have contributed to their linguistic legacy. These culturally significant practices were likely transmitted alongside their language as they migrated across Europe, influencing local customs and languages.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The source of Indo-European languages is traced to the Caucasus Lower Volga people in modern Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. |
| These languages are spoken by over 40% of the global population today. |
| Research utilizes DNA evidence to connect these early peoples to modern language families. |
| The studies confirm the existence of a linguistic continuum from the Yamnaya people to later populations across Europe and into Asia. |
| An unusual division in research findings arose from the Russia-Ukraine conflict, highlighting challenges in collaboration. |
| The findings unify historical linguistic data with genetic evidence, providing a clearer understanding of Indo-European language origins. |
Summary
The origins of the Indo-European languages are deeply intertwined with the archaeological and genetic history of ancient peoples from the Caucasus and Lower Volga regions. These groundbreaking studies reveal not only the location of these early speakers but also demonstrate how their migrations and interactions with neighboring cultures helped shape modern languages spoken globally. Understanding Indo-European language origins not only enriches our knowledge of linguistics but also connects us to our shared heritage.